Sparking caused by brush wear is a common problem in the operation of DC motors or wound rotor asynchronous motors. Sparks not only accelerate the wear of brushes and commutators/slip rings, but also generate electromagnetic interference and may even pose safety hazards. Morteng analyses the causes of the problem from the following:
Performance: Rapid brush wear and frequent replacement; noticeable sparks during operation, even burning the surface of the slip ring; brush jumping or vibration.
The main mechanical causes of sparks:
Poor brush contact: This is one of the most common causes.
Insufficient spring pressure: Spring ageing, deformation, or initial pressure settings that are too low can result in insufficient contact pressure between the brush and the commutator/slip ring, increasing contact resistance, causing the contact points to heat up, and making sparks more likely to occur during current commutation or micro-vibrations.
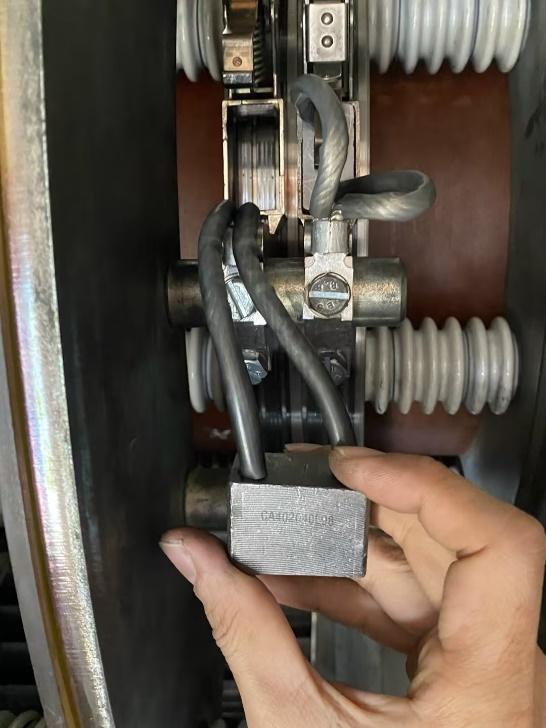

Excessive spring pressure: While excessive pressure may improve contact, it exacerbates mechanical friction and wear, generates excessive heat and carbon dust, and may damage the oxide film on the commutator surface, thereby increasing sparking.
Brushes stuck in the brush holder: Deformation of the brush holder, accumulation of deposits, mismatched brush dimensions, or wear on the sides of the brushes can cause them to move inflexibly within the brush holder, preventing them from properly following the minor vibrations or eccentricity of the commutator/slip rings, resulting in unstable contact.
Surface defects on the commutator/slip ring: Surface irregularities (scratches, pits, burn marks), excessive ellipticity/eccentricity, protruding mica sheets (commutator), or excessive axial movement can disrupt the smooth, continuous sliding contact between the brush and the rotating surface.
Improper brush installation: Brushes not correctly installed at the centre position or at the correct angle.
Excessive machine vibration: Vibration from the motor itself or the drive equipment is transmitted to the brush area, causing brush movement.
Uneven wear of the commutator/slip ring: Leading to an uneven surface.
Post time: Aug-27-2025





